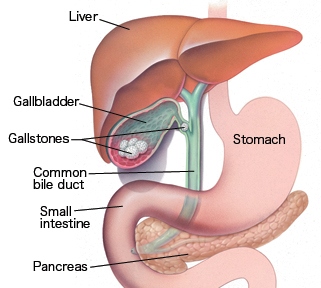
Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of gallbladder. It is carried out in case of stones or blockages in the gallbladder. It is also used in the case of inflammation or infection of the organ. The liver produces bile to digest food. When we eat, bile is added to the food as it passes into the small intestine. This bile is stored in the gallbladder. Bile breaks the fatty material in food into tiny fragments that help it to be more easily absorbed by the intestine. Once the gallbladder is removed, bile flows out of the liver through the hepatic ducts into the common bile duct and directly into the small intestine, instead of being stored in the gallbladder.
Symptoms
- Acute pain in the stomach or right abdomen area
- Low fever
- Nausea
- Bloated feeling
Solution
• The gallbladder is removed using laparoscopic procedure to reduce pain and other complications
Long-Term Complications
Gallstones can block the normal flow of bile if they move from the gallbladder and lodge itself in any of the ducts that carry bile from the liver to the small intestine. The ducts include the:
- Hepatic ducts – which carry bile out of the liver
- Cystic duct – which takes bile to and from the gallbladder
- Common bile duct – which takes bile from the cystic and hepatic ducts to the small intestine